Introduction
With rapid economic growth and urbanization, Vietnam has recognized the potential of waste-to-energy (WtE) technologies as a sustainable solution to address waste management issues and meet its growing energy demand. B&Company analyzed to explore the current state of the WtE market in Vietnam, covering emerging trends, notable projects with an emphasis on Japanese investment, and the future outlook for the sector.
The emergence of waste to energy in Viet Nam
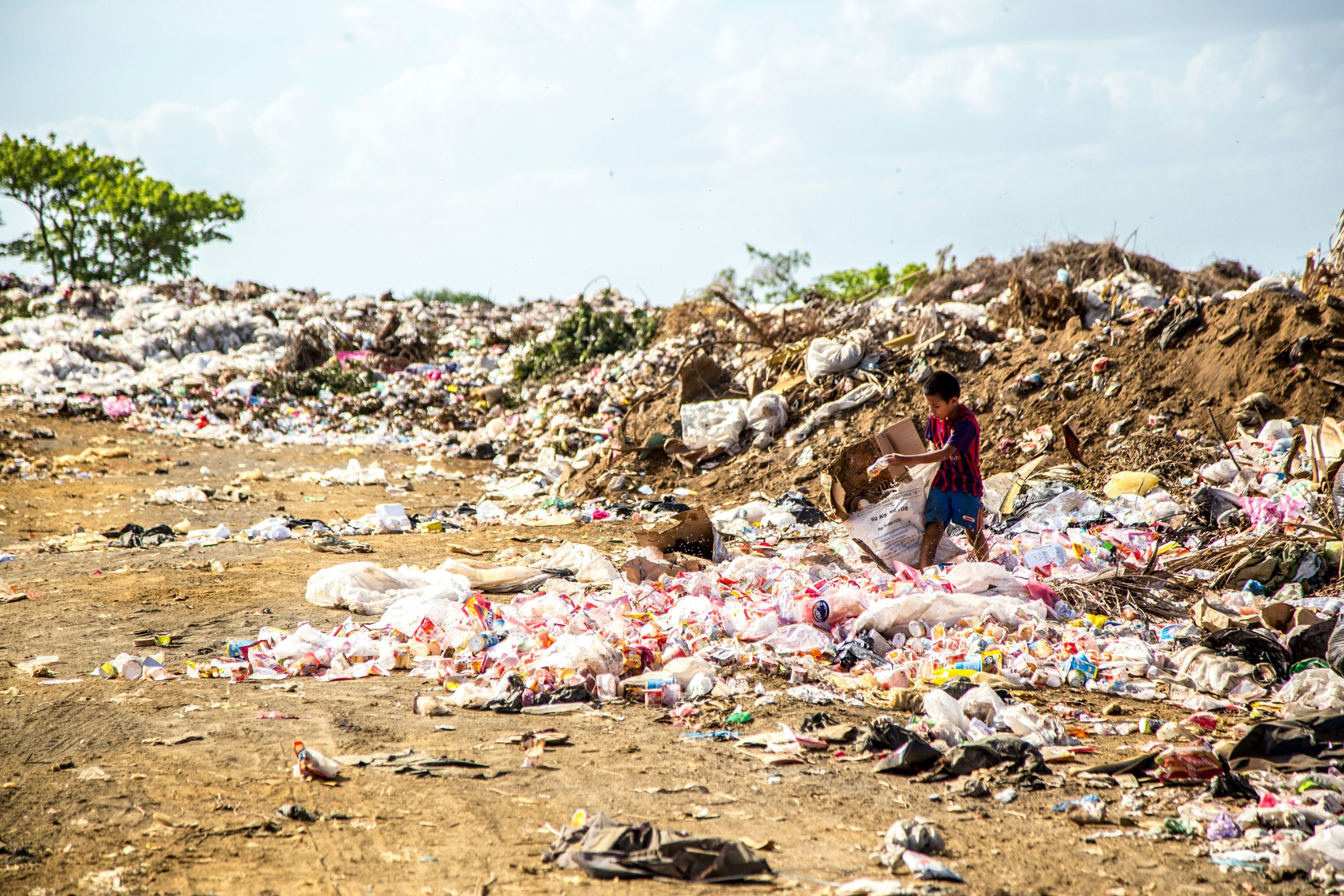
However, the landfilling method is becoming increasingly challenging as available land for this purpose continues to shrink. Given this situation, Waste-to-Energy is considered a solution that not only brings economic benefits but also makes significant and positive environmental contributions, thus creating opportunities for many businesses and investors.

Examples of landfill treatment in Vietnam. Source: PhapluatVietnam
There have been many government-supportive policies and incentives, creating a favorable environment for WtE development. The “National Strategy on Green Growth for the period 2021-2030, with a vision to 2050” emphasizes the development of green energy sources, including WtE, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and foster a circular economy. Additionally, the “Renewable Energy Development Strategy to 2030, with a Vision to 2050” sets targets for increasing the share of renewable energy, including WtE, in the country’s energy mix. In addition, given Vietnam’s large population and rapid urbanization, there would be a substantial amount of waste generated, providing a steady feedstock for WtE plants.
However, building WtE plants in Vietnam also faces several challenges. Due to the relatively new nature of WtE technology and its requirement for high-tech applications, it demands significant capital investment from businesses. Companies also face policy barriers, such as the regulation that ties WtE projects to power sector planning, causing delays as they must wait for approval. Investors further struggle with complex and lengthy procedures, particularly for public-private partnerships, with the investor selection process taking 1-2 years followed by various construction approvals. Project implementation is further slowed by multiple approval requirements from various ministries and the lack of specific guidelines for the Planning Law, which hinders power development planning.
Outstanding projects and Japanese investment
In recent years, the WtE market in Vietnam has been gaining momentum, with several projects under development across the country. According to a report by the Environmental Pollution Control Department (2023), Vietnam currently has 15 WtE plants under construction some of which have already begun generating electricity[3], such as the Waste Treatment Plant of EB Environmental Energy Company with a capacity of 400 tons/day in Can Tho City; or Soc Son Waste-to-Energy Plant with a capacity of 4,000 tons/day in Hanoi.

Soc Son WtE Plant. Source: VNA
These are also projects that received Japanese investment. The Can Tho WtE plant was constructed with financial support from the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) and technical expertise from Hitachi Zosen Corporation. Similarly, the Hanoi WtE plant, one of the largest WtE facilities in Southeast Asia and Vietnam, was developed with investment from the Japanese conglomerate Sumitomo Corporation. In addition to Japan, Korea also has investments in this field, notably the Municipal Solid Waste and Industrial WtE (GCEP) Plant by Green Star Environmental Co., Ltd. and Chosun Refractories ENG Korea (capacity 500 tons/day), and the Waste-to-Energy project in Long An and Kien Giang provinces with the cooperation of BCG Energy, SK Ecoplant (a subsidiary of SK Group, South Korea), and SLC (Sudokwon Landfill Site Management Corp, South Korea).
Outlook of WtE in Vietnam
The future outlook for the WtE market in Vietnam is promising, driven by the government’s commitment to sustainable waste management and clean energy development. WIn addition, while the number of projects is still limited and demand is still very high, Japan still has a lot of room for investment in WtE projects, especially in the context of the growing focus and priority on green transformation and transition to green energy.
References
[1] KinhteDoThi (2024), “New ways for environmental issues”. <https://kinhtedothi.vn/huong-di-moi-cho-bai-toan-moi-truong.html>
[2] Same as above
[3] https://quanly.moitruongvadothi.vn/15/27092/Viet-Nam-hien-co-bao-nhieu-nha-may-dot-rac-phat-dien.aspx
| B&Company有限公司
自 2008 年以来,第一家专门在越南从事市场研究的日本公司。我们提供广泛的服务,包括行业报告、行业访谈、消费者调查、商业配对。此外,我们最近还开发了一个包含越南 900,000 多家公司的数据库,可用于搜索合作伙伴和分析市场。 如果您有任何疑问,请随时与我们联系。 信息@b-company.jp + (84) 28 3910 3913 |
阅读其他文章